Although the national price of gas is a bit lower than it was a year ago, the optional standard mileage rate used to calculate the deductible cost of operating an automobile for business will be going up in 2023. The IRS recently announced that the 2023 cents-per-mile rate for the business use of a car, van, pickup or panel truck is 65.5 cents. These rates apply to electric and hybrid-electric automobiles, as well as gasoline and diesel-powered vehicles. In 2022, the business cents-per-mile rate for the second half of the year (July 1 – December 31) was 62.5 cents per mile, and for the first half of the year (January 1 – June 30), it was 58.5 cents per mile. How rate calculations are done The 3-cent increase...

On January 10, 2023, IRS news release IR-2023-03 announced that California storm victims now have until May 15, 2023, to file various federal individual and business tax returns and make tax payments. The IRS is offering relief to any area designated by the Federal Emergency Management Agency (FEMA). This means that individuals and households that reside or have a business in Alameda, Colusa, Contra Costa, El Dorado, Fresno, Glenn, Humboldt, Kings, Lake, Los Angeles, Madera, Marin, Mariposa, Mendocino, Merced, Mono, Monterey, Napa, Orange, Placer, Riverside, Sacramento, San Benito, San Bernardino, San Diego, San Francisco, San Joaquin, San Luis Obispo, San Mateo, Santa Barbara, Santa Clara, Santa Cruz, Solano, Sonoma, Stanislaus, Sutter, Tehama, Tulare, Ventura, Yolo and Yuba counties qualify for tax relief. On January 11, 2023, the...
If you’re considering converting your C corporation to an S corporation, be aware that there may be tax implications if you’ve been using the last in, first out (LIFO) inventory method. That’s because of the LIFO recapture income that will be triggered by converting to S corporation status. Consider computing in advance what the tax on this recapture would be and to see what planning steps might be taken to minimize it. Inventory reporting As you’re aware, your corporation has been reporting a lower amount of taxable income under LIFO than it would have under the first in, first out (FIFO) method. The reason: The inventory taken into account in calculating the cost of goods sold under LIFO reflects current costs, which are usually higher. This benefit of...
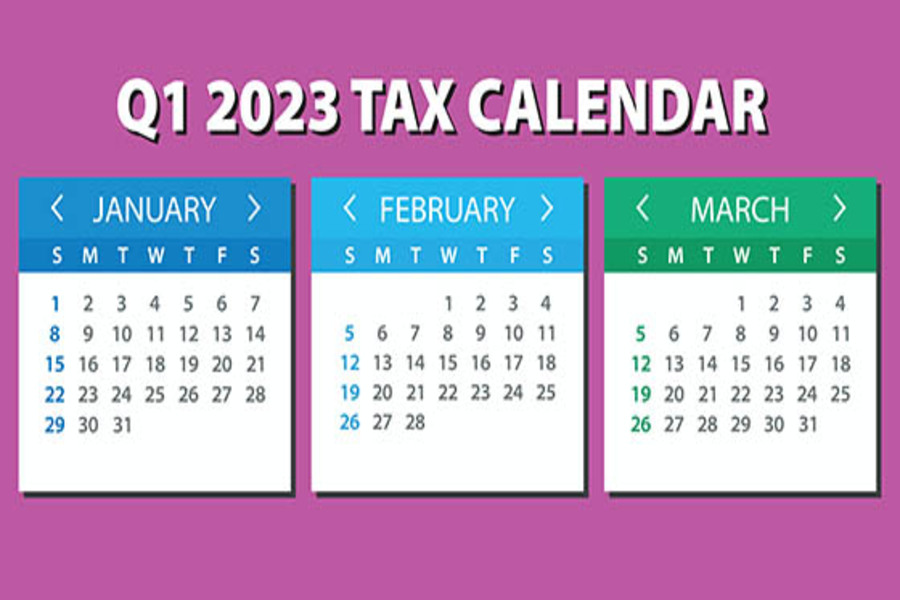
Here are some of the key tax-related deadlines affecting businesses and other employers during the first quarter of 2023. Keep in mind that this list isn’t all-inclusive, so there may be additional deadlines that apply to you. If you have questions about filing requirements, contact us. We can ensure you’re meeting all applicable deadlines. January 17 (The usual deadline of January 15 is on a Sunday and January 16 is a federal holiday) Pay the final installment of 2022 estimated tax. Farmers and fishermen: Pay estimated tax for 2022. If you don’t pay your estimated tax by January 17, you must file your 2022 return and pay all tax due by March 1, 2023, to avoid an estimated tax penalty. January 31 File 2022 Forms W-2, “Wage...
If you own a business, you may wonder if you’re eligible to take the qualified business income (QBI) deduction. Sometimes this is referred to as the pass-through deduction or the Section 199A deduction. The QBI deduction is: Available to owners of sole proprietorships, single member limited liability companies (LLCs), partnerships, and S corporations, as well as trusts and estates. Intended to reduce the tax rate on QBI to a rate that’s closer to the corporate tax rate. Taken “below the line.” In other words, it reduces your taxable income but not your adjusted gross income. Available regardless of whether you itemize deductions or take the standard deduction. Taxpayers other than corporations may be entitled to a deduction of up to 20% of their QBI. For 2022, if...
As posted to IRS.gov as Tax Tip 2022-117 on 8/2/2022 A business might pay an independent contractor and an employee for the same or similar work, but there are key legal differences between the two. It is critical for business owners to correctly determine whether the people providing services are employees or independent contractors. An employee is generally considered anyone who performs services, if the business can control what will be done and how it will be done. What matters is that the business has the right to control the details of how the worker's services are performed. Independent contractors are normally people in an independent trade, business or profession in which they offer their services to the public. Independent contractor vs. employee Whether a worker is an independent...
If you’re launching a new business venture, you’re probably wondering which form of business is most suitable. Here is a summary of the major advantages and disadvantages of doing business as a C corporation. A C corporation allows the business to be treated and taxed as a separate entity from you as the principal owner. A properly structured corporation can protect you from the debts of the business yet enable you to control both day-to-day operations and corporate acts such as redemptions, acquisitions and even liquidations. In addition, the corporate tax rate is currently 21%, which is lower than the highest noncorporate tax rate. Following formalities In order to ensure that a corporation is treated as a separate entity, it’s important to observe various formalities required by your state....
These days, most businesses have some intangible assets. The tax treatment of these assets can be complex. What makes intangibles so complicated? IRS regulations require the capitalization of costs to: Acquire or create an intangible asset, Create or enhance a separate, distinct intangible asset, Create or enhance a “future benefit” identified in IRS guidance as capitalizable, or “Facilitate” the acquisition or creation of an intangible asset. Capitalized costs can’t be deducted in the year paid or incurred. If they’re deductible at all, they must be ratably deducted over the life of the asset (or, for some assets, over periods specified by the tax code or under regulations). However, capitalization generally isn't required for costs not exceeding $5,000 and for amounts paid to create or facilitate the creation of...
Businesses shut down for many reasons. Some of the reasons that businesses shutter their doors: An owner retirement, A lease expiration, Staffing shortages, Partner conflicts, and Increased supply costs. If you’ve decided to close your business, we’re here to assist you in any way we can, including taking care of the various tax obligations that must be met. For example, a business must file a final income tax return and some other related forms for the year it closes. The type of return to be filed depends on the type of business you have. Here’s a rundown of the basic requirements. Sole Proprietorships. You’ll need to file the usual Schedule C, “Profit or Loss from Business,” with your individual return for the year you close the business. You...
These days, most businesses buy or lease computer software to use in their operations. Or perhaps your business develops computer software to use in your products or services or sells or leases software to others. In any of these situations, you should be aware of the complex rules that determine the tax treatment of the expenses of buying, leasing or developing computer software. Software you buy Some software costs are deemed to be costs of “purchased” software, meaning it’s either: Non-customized software available to the general public under a nonexclusive license, or Acquired from a contractor who is at economic risk should the software not perform. The entire cost of purchased software can be deducted in the year that it’s placed into service. The cases in which the...