Operating as an S corporation may help reduce federal employment taxes for small businesses in the right circumstances. Although S corporations may provide tax advantages over C corporations, there are some potentially costly tax issues that you should assess before making a decision to switch. Here’s a quick rundown of the most important issues to consider when converting from a C corporation to an S corporation: Built-in gains tax Although S corporations generally aren’t subject to tax, those that were formerly C corporations are taxed on built-in gains (such as appreciated property) that the C corporation has when the S election becomes effective, if those gains are recognized within 5 years after the corporation becomes an S corporation. This is generally unfavorable, although there are situations where the S election...

The federal government is helping to pick up the tab for certain business meals. Under a provision that’s part of one of the COVID-19 relief laws, the usual deduction for 50% of the cost of business meals is doubled to 100% for food and beverages provided by restaurants in 2022 (and 2021). So, you can take a customer out for a business meal or order take-out for your team and temporarily write off the entire cost — including the tip, sales tax and any delivery charges. Basic rules Despite eliminating deductions for business entertainment expenses in the Tax Cuts and Jobs Act (TCJA), a business taxpayer could still deduct 50% of the cost of qualified business meals, including meals incurred while traveling away from home on business. (The...
If you operate a business, or you’re starting a new one, you know you need to keep records of your income and expenses. Specifically, you should carefully record your expenses in order to claim all of the tax deductions to which you’re entitled. And you want to make sure you can defend the amounts reported on your tax returns in case you’re ever audited by the IRS. Be aware that there’s no one way to keep business records. But there are strict rules when it comes to keeping records and proving expenses are legitimate for tax purposes. Certain types of expenses, such as automobile, travel, meals and home office costs, require special attention because they’re subject to special recordkeeping requirements or limitations. Here are two recent court...
Typically, businesses want to delay recognition of taxable income into future years and accelerate deductions into the current year. But when is it prudent to do the opposite? And why would you want to? One reason might be tax law changes that raise tax rates. There have been discussions in Washington about raising the corporate federal income tax rate from its current flat 21%. Another reason may be because you expect your non-corporate pass-through entity business to pay taxes at higher rates in the future, because the pass-through income will be taxed on your personal return. There have also been discussions in Washington about raising individual federal income tax rates. If you believe your business income could be subject to tax rate increases, you might want to accelerate...
If your business doesn’t already have a retirement plan, now might be a good time to take the plunge. Current retirement plan rules allow for significant tax-deductible contributions. For example, if you’re self-employed and set up a SEP-IRA, you can contribute up to 20% of your self-employment earnings, with a maximum contribution of $61,000 for 2022. If you’re employed by your own corporation, up to 25% of your salary can be contributed to your account, with a maximum contribution of $61,000. If you’re in the 32% federal income tax bracket, making a maximum contribution could cut what you owe Uncle Sam for 2022 by a whopping $19,520 (32% times $61,000). More options Other small business retirement plan options include: 401(k) plans, which can even be set up for...
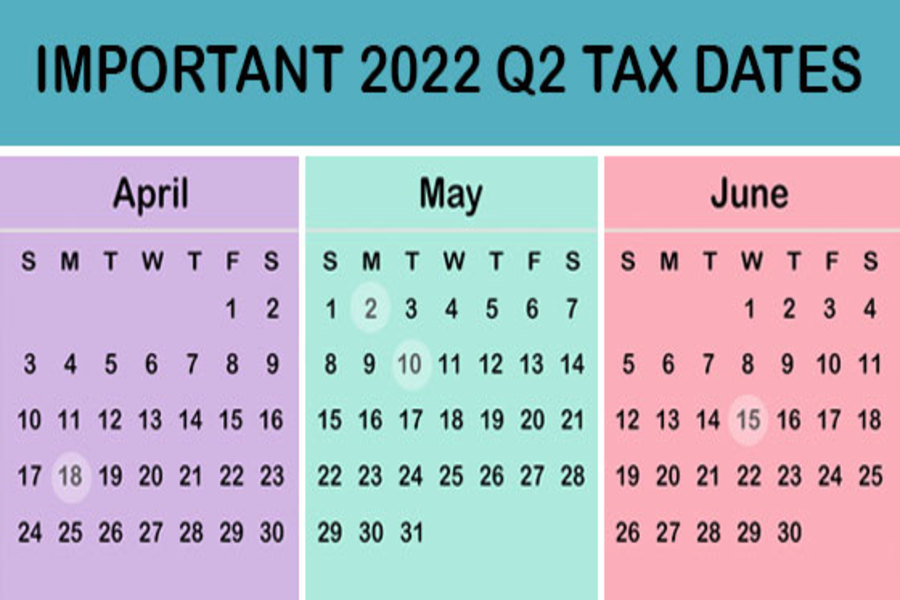
Here are some of the key tax-related deadlines that apply to businesses and other employers during the second quarter of 2022. Keep in mind that this list isn’t all-inclusive, so there may be additional deadlines that apply to you. Contact us to ensure you’re meeting all applicable deadlines and to learn more about the filing requirements. April 18 If you’re a calendar-year corporation, file a 2021 income tax return (Form 1120) or file for an automatic six-month extension (Form 7004) and pay any tax due. Corporations pay the first installment of 2022 estimated income taxes. For individuals, file a 2021 income tax return (Form 1040 or Form 1040-SR) or file for an automatic six-month extension (Form 4868) and paying any tax due. (See June 15 for...
In today’s economy, many small businesses are strapped for cash. They may find it beneficial to barter or trade for goods and services instead of paying cash for them. Bartering is the oldest form of trade and the internet has made it easier to engage with other businesses. But if your business gets involved in bartering, be aware that the fair market value of goods that you receive in bartering is taxable income. And if you exchange services with another business, the transaction results in taxable income for both parties. How it works Here are some examples: A computer consultant agrees to exchange services with an advertising agency. A plumber does repair work for a dentist in exchange for dental services. In these cases, both parties are taxed...
The credit for increasing research activities, often referred to as the research and development (R&D) credit, is a valuable tax break available to eligible businesses. Claiming the credit involves complex calculations, which we can take care of for you. But in addition to the credit itself, be aware that the credit also has two features that are especially favorable to small businesses: Eligible small businesses ($50 million or less in gross receipts) may claim the credit against alternative minimum tax (AMT) liability. The credit can be used by certain even smaller startup businesses against the employer’s Social Security payroll tax liability. Let’s take a look at the second feature. Subject to limits, you can elect to apply all or some of any research tax credit that...
You may have wondered why, in a given year, you may be taxed on more S corporation income than was distributed to you from the S corporation in which you are a shareholder. The answers lies in the way S corporations and their shareholders are taxed. But before explaining those rules, be assured you that when you are taxed on undistributed income, you won't be taxed again if and when the income ultimately is paid to you. Unlike a regular or C corporation, an S corporation generally isn't subject to income tax (California does charge a 1.5% entity-level tax). Instead, each shareholder is taxed on the corporation's earnings, whether or not the earnings are distributed. Similarly, if an S corporation has a loss, the loss is passed...
Back in 2017, the Tax Cuts and Jobs Act was signed into law which instituted a cap on the amount of state and local taxes (SALT) that individuals could report as Itemized Deductions on Schedule A. Starting with the 2018 tax year, the maximum SALT deduction available was $10,000. Previously, there was no limit. Since then, roughly 20 states have come up with workarounds intended to negate, or at least mitigate the effect of the SALT limitation. In 2021 California passed AB 150, which provides that, in the taxable years 2021-2025, a so-called "qualified entity" (a S corporation, partnership, or LLC taxed as a partnership or S corporation) to make an election to pay a new pass-through entity (PTE) elective tax equal to 9.3% of its...