If you’re planning to start a business or thinking about changing your business entity, you need to determine what will work best for you. Should you operate as a C corporation or a pass-through entity such as a sole-proprietorship, partnership, limited liability company (LLC) or S corporation? There are many issues to consider. Currently, the corporate federal income tax is imposed at a flat 21% rate, while individual federal income tax rates currently begin at 10% and go up to 37%. The difference in rates can be alleviated by the qualified business income (QBI) deduction that’s available to eligible pass-through entity owners that are individuals, and some estates and trusts. Individual rate caveats: The QBI deduction is scheduled to end in 2026, unless Congress acts to extend it, while...

The Social Security Administration recently announced that the wage base for computing Social Security tax will increase to $168,600 for 2024 (up from $160,200 for 2023). Wages and self-employment income above this threshold aren’t subject to Social Security tax. Basic details The Federal Insurance Contributions Act (FICA) imposes two taxes on employers, employees and self-employed workers — one for Old Age, Survivors and Disability Insurance, which is commonly known as the Social Security tax, and the other for Hospital Insurance, which is commonly known as the Medicare tax. There’s a maximum amount of compensation subject to the Social Security tax, but no maximum for Medicare tax. For 2024, the FICA tax rate for employers will be 7.65% — 6.2% for Social Security and 1.45% for Medicare (the same...
Do you use an automobile in your trade or business? If so, you may question how depreciation tax deductions are determined. The rules are complicated, and special limitations that apply to vehicles classified as passenger autos (which include many pickups and SUVs) can result in it taking longer than expected to fully depreciate a vehicle. Depreciation is built into the cents-per-mile rate First, be aware that separate depreciation calculations for a passenger auto only come into play if you choose to use the actual expense method to calculate deductions. If, instead, you use the standard mileage rate (65.5 cents per business mile driven for 2023), a depreciation allowance is built into the rate. If you use the actual expense method to determine your allowable deductions for a passenger...
Ever wonder how IRS examiners know about different industries so they can audit various businesses? They generally do research about specific industries and issues on tax returns by using IRS Audit Techniques Guides (ATGs). A little-known fact is that these guides are available to the public on the IRS website. In other words, your business can use the same guides to gain insight into what the IRS is looking for in terms of compliance with tax laws and regulations. Many ATGs target specific industries, such as construction, aerospace, art galleries, architecture and veterinary medicine. Other guides address issues that frequently arise in audits, such as executive compensation, passive activity losses and capitalization of tangible property. Issues unique to certain taxpayers IRS auditors need to examine all different types...
If you read the Internal Revenue Code (and you probably don’t want to!), you may be surprised to find that most business deductions aren’t specifically listed. For example, the tax law doesn’t explicitly state that you can deduct office supplies and certain other expenses. Some expenses are detailed in the tax code, but the general rule is contained in the first sentence of §162, which states you can write off “all the ordinary and necessary expenses paid or incurred during the taxable year in carrying on any trade or business.” Basic definitions In general, an expense is ordinary if it’s considered common or customary in the particular trade or business. For example, insurance premiums to protect a store would be an ordinary business expense in the retail...
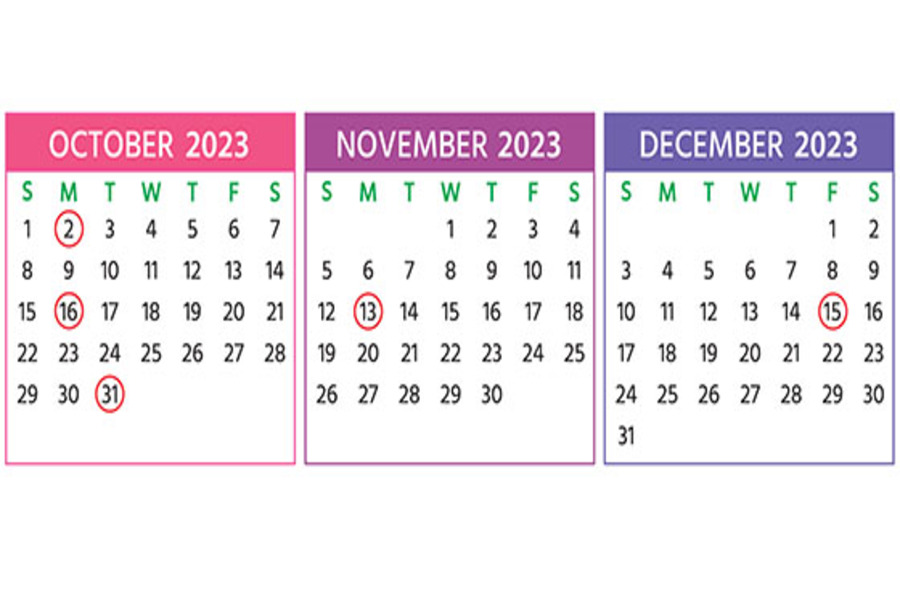
Here are some of the key tax-related deadlines affecting businesses and other employers during the fourth quarter of 2023. Keep in mind that this list isn’t all-inclusive, so there may be additional deadlines that apply to you. Contact us to ensure you’re meeting all applicable deadlines and to learn more about the filing requirements. Note: Certain tax-filing and tax-payment deadlines may be postponed for taxpayers who reside in or have businesses in federally declared disaster areas. Monday, October 2 The last day you can initially set up a SIMPLE IRA plan, provided you (or any predecessor employer) didn’t previously maintain a SIMPLE IRA plan. If you’re a new employer that comes into existence after October 1 of the year, you can establish a SIMPLE IRA plan as...
In recent years, merger and acquisition activity has been strong in many industries. If your business is considering merging with or acquiring another business, it’s important to understand how the transaction will be taxed under current law. Stocks vs. assets From a tax standpoint, a transaction can basically be structured in two ways: 1. Stock (or ownership interest) sale. A buyer can directly purchase a seller’s ownership interest if the target business is operated as a C or S corporation, a partnership, or a limited liability company (LLC) that’s treated as a partnership for tax purposes. The now-permanent 21% corporate federal income tax rate under the Tax Cuts and Jobs Act (TCJA) makes buying the stock of a C corporation somewhat more attractive. Reasons: The corporation will pay less tax and...
Do you and your spouse together operate a profitable unincorporated small business? If so, you face some challenging tax issues. The partnership issue An unincorporated business with your spouse is classified as a partnership for federal income tax purposes, unless you can avoid that treatment. Otherwise, you must file an annual partnership return, on Form 1065. In addition, you and your spouse must be issued separate Schedule K-1s, which allocate the partnership’s taxable income, deductions and credits between the two of you. This is only the beginning of the unwelcome tax compliance tasks. The self-employment (SE) tax problem The SE tax is how the government collects Social Security and Medicare taxes from self-employed individuals. For 2023, the SE tax consists of 12.4% Social Security tax on the first $160,200...
Are employees at your business traveling and frustrated about documenting expenses? Or perhaps you’re annoyed at the time and energy that goes into reviewing business travel expenses. There may be a way to simplify the reimbursement of these expenses. In Notice 2023-68, the IRS announced the fiscal 2024 special “per diem” rates that became effective October 1, 2023. Taxpayers can use these rates to substantiate the amount of expenses for lodging, meals and incidentals when traveling away from home. (Taxpayers in the transportation industry can use a special transportation industry rate.) Basics of the method A simplified alternative to tracking actual business travel expenses is to use the “high-low” per diem method. This method provides fixed travel per diems. The amounts, provided by the IRS, vary from locality to...
The Tax Cuts and Jobs Act liberalized the rules for depreciating business assets. However, the amounts change every year due to inflation adjustments. And due to high inflation, the adjustments for 2023 were big. Here are the numbers that small business owners need to know. §179 deductions For qualifying assets placed in service in tax years beginning in 2023, the maximum §179 deduction is $1.16 million. But if your business puts in service more than $2.89 million of qualified assets, the maximum §179 deduction begins to be phased out. Eligible assets include depreciable personal property such as equipment, computer hardware and peripherals, vehicles and commercially available software. §179 deductions can also be claimed for real estate qualified improvement property (QIP), up to the maximum allowance of $1.16 million. QIP...